1. Floating-point number
- 소수를 포함해 매우 큰 수와 작은 수 표현
1) Notation
- decimal : 1.0 x 10^(-9) (normalized number)
- binary : 1.0(2) x 2^(-1)
2. floating-point representation

- Fraction과 exponent는 한 word(32 bits) 안에서 표현.
- Fraction을 표현하는데 많은 비트를 사용할 수록 정확도(precision) 증가
- Exponent에 많은 비트를 사용하면 표현할 수 있는 숫자 범위(range) 증가
- overflow : exponent field로 표현할 수 없이 큰 양수가 들어올 때
- underflow : exponent filed에 표현할 수 없이 큰 음수가 들어올 때
- overflow와 underflow를 줄이기 위해 double precision 사용
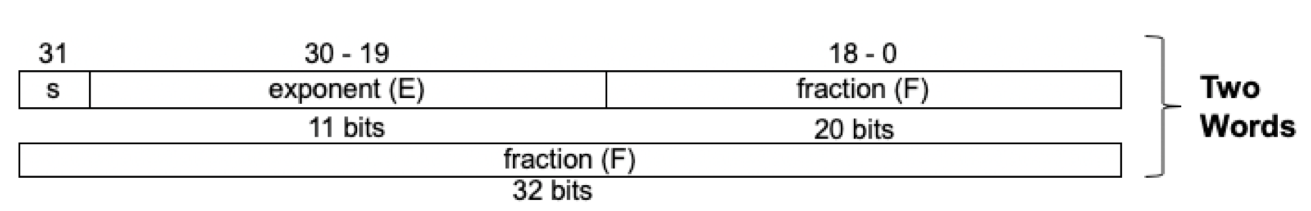
3. IEEE 754 floationg-point format

1) s : sign bit(0 or 1)
2) significand :
1+fraction (Normalized number에서 정수 부분은 항상 1이기 때문에 fraction은 1을 제외한 소수 부분만 나타냄.
(더 많은 비트의 significand 표현가능. Ex : single precision에서 24bits 표현가능(암시적인 1 bit와 fraction 23 bits))
3) Exponent :
actual exponent + bias = biased exponent (biased exponent로 바꿈으로써 unsigned로 표현 -> 정렬 시 간단)
(single precision : 127, double precision : 1203)
Biased exponent

(in single precision) Actual exponent : -128 ~ 127, biased exponent : -1 ~ 254
Biased exponen의 몇 가지 표현은 특정한 값을 표현하기 위해 예약되어 있음 1+fraction
|
Single precision |
Double precision |
Object represented |
||
|
Exponent |
Fraction |
Exponent |
Fraction |
|
|
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
|
0 |
Nonzero |
0 |
Nonzero |
Denormalized number |
|
1-254 |
Anything |
1-2046 |
Anything |
floating-point number |
|
255 |
0 |
2047 |
0 |
Infinity |
|
255 |
Nonzero |
2047 |
Nonzero |
nan |
4) Single precision에서 표현 범위
Smallest value
Exponent : 00000001 -> actual exponent = 1 – 127 : -126
Fraction : 00…0000 -> significand = 1 + fraction : 1.0
-1.000….0000(2) * 2^-126
Largest value
Exponent : 1111110 -> actual exponent = 254 – 127 : 127
Fraction : 11…1111 -> significand = 1 + fraction : 1.1111…1
+1.1111….1111(2) * 2^127
-1.000….0000(2) * 2^-126 ~ +1.1111….1111(2) * 2^127
4. Floating point addition(binary)
ex) 0.5 + (-0.4375)
(binarization) 1.0 * 2^-1 – 1.11 * 2^-2
1)Align(지수가 높은 수의 지수로 통일해줌)
1.0 * 2^-1 – 0.111 * 2^-1
2)Add significands(두 수를 더함)
0.001 * 2^-1
3)Normalize, check over/underflow
1.0 * 2^-4
4)Round(반올림)

1. 더 작은 지수를 찾는다.
2. 지수의 차 계산
3. 더 작은 수의 significand를 지수의 차 만큼 shift right
4. 두 significand의 뺄셈 연산 수행
5. Significand의 결과값을 통해 exponent를 계산하고, normalization 수행
6. Fraction 계산 ( significand – 1)
7. Overflow 또는 underflow 발생 시 round
5. Floating point support in MIPS ISA
1) Floating point addition and subtraction
-add.s, add.d, sub.s, sub.d (s: single precision, d: double precision)
2) Floating point multiplication and division
-mul.s, mul.d, div.s, div.d
3) Floating point data transfer operation
- lwc1, swc1
4) Floating point comparison
-c.eq.s, c.eq.d, c.lt.s, c.lt.d… (condition code flag를 0 또는 1로 설정)
5) Floating point branch true/false
- condition code flag 기반
- bc1t : condition code flag가 true면 branch
- bc1f : condition code flag가 false면 branch
6) Floating point register 구분
-$f0, $f1,…, $f31( 총 32개 )
-Double precision은 floating point register 쌍으로 사용 ($f0,$f1), ($f2,$f3), …
-Floating point instruction은 floating point register만 사용
'CS > Computer Architecture' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Language of the Computer (0) | 2019.12.23 |
|---|---|
| Computer Abstraction and Technology (1) | 2019.12.22 |
| Processor - Datapath (0) | 2019.12.17 |
| Memory Hierarchy (0) | 2019.12.16 |
| Processor - logic design basics (0) | 2019.12.16 |




댓글